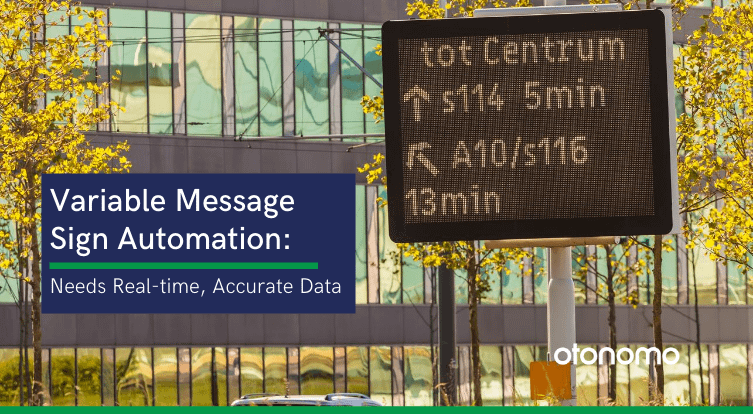
Variable Message Signs (VMS) Perform Multiple Traffic Management Roles
Variable message signs, also known as dynamic message signs, changeable message signs (CMS), or matrix signs, have become a fixture on key highways across the world. They are a popular traffic management solution. A 2017 survey by the U.S. Federal Highway Administration found that 85% of U.S. states have deployed some variable message signs to communicate road condition information; 50% have completed statewide deployments. Similarly, the European Union and United Kingdom have widely adopted variable message signs, developing standards to make usage and messaging more consistent across countries.
Variable message signs can communicate several types of information:
- Hazardous weather conditions such as wind, wet pavement, or ice
- Traffic incidents or events such as accidents, vehicle breakdowns in lanes, construction work, or slowdowns
- Informative information such as travel times to a point of interest
- Safety-related messages such as reminders not to text and drive
- Non-traffic related public messages such as missing person alerts and even fuel price comparisons
Variable Message Signs Have a Measurable Impact
A large body of research supports the safety and effectiveness of variable message signs. For example, primary and secondary research conducted on behalf of the Maryland Department of Transportation demonstrated that variable message signs do not increase congestion or accidents. In the on-off comparison study, the least number of accidents near the variable message signs occurred at the times when signs were being displayed. Other studies in the European Union and the State of Minnesota report on the effectiveness of variable message signs and positive driver perceptions.
Transportation Agencies Face a Common Set of Challenges
In our connected world, drivers expect variable message signing to be as consistent and accurate as the information they receive from apps like Google Maps or Waze. That can be easier said than done. The most common challenges cited by U.S. state agencies with respect to variable message signs are:
- Inaccurate forecasting or false alarms
- Inadequate assets (i.e. sensors and other real-time traffic data sources) in affected areas
- Issues with messaging
- Timely message updates
Variable Message Sign Automation Requires Precise, Real-Time Triggers
Today, a significant proportion of variable message signage is manually updated, with support from road weather management tools and technologies such as environmental sensor stations (ESS). For example, more than half of U.S. states participating in a Minnesota Department of Transportation survey use mostly manual methods, while just one state uses a mostly automated method.
Increasing the automation in these systems would require a precise set of triggers that represent a hazardous condition, such as a decrease in pavement temperature or multiple sudden braking events. The triggers would have to update very quickly to have the desired impact on driver behavior.
How Car Data Can Help
As connected cars become a significant proportion of traffic on the road, transportation agencies now have a valuable, cost-effective source of information about what’s happening on the roads. Car data can supplement existing data sources such as ESSs, pavement sensors, and RFID toll tags. More importantly, they can increase data coverage to virtually every point on the road and provide new information that has not been accessible to transportation agencies in the past such as:
- Rain intensity
- Vehicle breakdowns
- Hard braking events
The Next Step: From Variable Message Signs to Infrastructure-to-Vehicle Communication
At their next stage of evolution, variable message signs could use wireless technology to communicate directly with the car, either providing an in-vehicle message or verbal alert to a potentially hazardous condition. This type of infrastructure-to-vehicle (I2V) communication would address challenges with sign placement, limited visibility, or incomplete driver attention.
Find New Ways to Improve Variable Message Signs Now
The Otonomo Platform provides access to crowd data from millions of connected vehicles in more than 70 countries, including traffic data and road incidents or weather hazards. The data is cleansed, normalized, and enriched so it’s easier to gain actionable insights. And with a standards-based API, the Otonomo Platform has a straightforward API to integrate into existing road and weather information systems.
You can contact us for more information or see these datasets for yourself by starting a 30-day free trial of the Otonomo Platform.